Collets 101: The Definitive Guide
Overview
Collets 101: The Definitive Guide covers five popular collet series: ER collets, TG collets, DA collets, AF collets, and RDO collets. In each section, you will find: recommended uses for each type of collet, along with accuracy metrics (T.I.R.), and tips for how to care for each collet system. If you are new to all of this, please refer to the FAQ & Glossary at the end of this guide for some answers to common beginner questions.
5 Collet Types & Recommended Applications
RDG/TG Collet |
RDO Collet |
RD/ER Collet |
RDF/AF Collet |
RDA/DA Collet |
| Milling Drilling Rigid Tapping Coolant Through |
Woodworking Routers European Systems |
Drilling Milling Rigid Tapping Tapping (with Length Compensation) Reaming Boring Coolant Through External Coolant Through High Precision Grinding |
Drilling Milling Coolant Through (in 50, 75 & 100 series) |
Drilling |
ER Collets: The Best Toolholding Collet System
The RD/ER Collet System is the most versatile Toolholding System for any operation utilizing a round shank cutting tool in a machining or turning center. This includes drilling, milling, tapping, reaming and boring. RD/ER Collets are commonly known in the industry as ER, ESX, DR, BR, and VSAC Collets.
RECOMMENDED USES OF ER COLLETS
ER collets are recommended for Drilling, Milling, Rigid Tapping, Tapping (with Length Compensation), Reaming, Boring, Coolant Through, External Coolant Through, and High Precision Grinding.
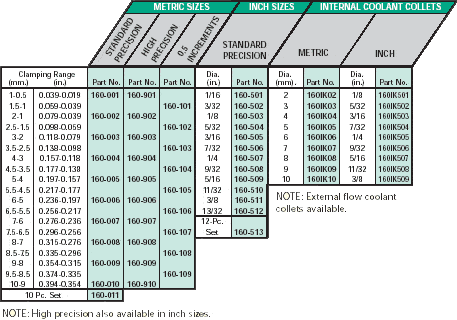
RD/ER Collets are available in the following series ranges to maximize efficiency in most applications:
| Series RD 8 RD 11 RD 12 RD 16 RD 20 RD 25 RD 32 |
Inch Capacity 1/32-3/16 1/16-1/4 1/32-1/4 1/16-13/32 1/16-1/2 1/16-5/8 3/32-3/4 |
Metric Capacity .25mm-5.0mm .25mm-7.0mm .5mm-7.0mm .25mm-10.0mm .5mm-13mm .5mm-16mm .2mm-20mm |
 |
HIGHEST ACCURACY: RD/ER COLLET CONCENTRICITY – PER DIN 6499
METRIC
|
INCHES
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ACCURACY OF ER COLLETS
The RD / ER collet system is the only popular Toolholding system in which all components (ER chucks, ER collets and ER clamping nuts) are standardized by DIN 6499. Most Toolholding Collet systems state the collet is .0005 or .001 T.I.R. but, that does not mean that this is the accuracy one will achieve on the cutting tool when mounted into the chuck. The accuracy of the RD/ER assembly is guaranteed to conform to the DIN 6499 Table.
ER collet systems are truly interchangeable. All manufacturers of the ER collet system should conform to the DIN6499 standard. This becomes important to users that may have toolholding systems from different Toolholding System Manufacturers. As tools are taken out of the tool crib and reassembled for different jobs, if all the RD/ER system components are in good condition, and are from Quality Toolholding System Manufacturers, the collet and tool should achieve the DIN 6499 accuracy.
Mixing components of Toolholding Systems other than RD/ER can have varying results. While other Toolholding systems may be “interchangeable”, none of the Toolholding Systems Manufacturers know the tolerances and specifications others are using for all of the components.
HOW TO USE ENDMILLS
When using endmills or any round shank cutting tool, collets and collet chucks centralize the cutting tool, unlike conventional sidelock endmill holders that push the tool to the side of the bore of the holder with a set screw. This method creates a small contact area on the cutting tool and shifts the cutting tool from the true centerline of the Machine spindle. With the cutting tool off-center, the cutting tool edges have an uneven load and will wear out prematurely. Collets and Collet Chucks centralizing the cutting tool will result in increased tool life, higher feed rates, better workpiece accuracy and enhanced workpiece finish. Carbide endmills are usually not supplied with a weldon or locking flat for side lock endmill holders. This is because they are not designed to be used in side lock endmill holders. Many Machinists hand grind a locking flat on to the shank of the carbide end mills to use them in side lock holders, perhaps it would be better to use them in the type of tool that they are designed to be used in.
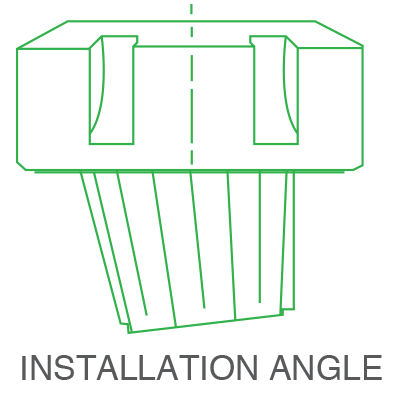
METHOD OF INSERTION & RELEASE FOR RD/ER COLLETS
| INSERTING
|
RELEASING
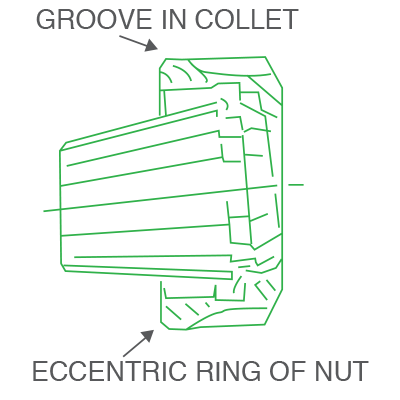
Hold nut in vertical position and remove nut at an angle. Collet is automatically withdrawn from chuck by excentric ring of nut when unscrewed. |
CARE AND USE OF ER COLLET SYSTEMS
The ER chuck, ER collet and ER nut must be thoroughly cleaned before assembling to maintain accuracy. Use a benchtop ultrasonic cleaner to dislodge fine chips and debris. You can also use a bottle-type brush to clean the inner diameter of the collet and a toothbrush-style brush to clean the exterior.
Once assembled, a normal machining environment will not affect the ER toolholding assembly. The ER collet must be installed into the nut (see assembly instructions) before engagement with the collet chuck to ensure the ER collet is seated into the 30 degree concave angle of the nut. Putting the ER collet into the chuck and then installing the nut will result in a condition that the eccentric ring of nut will engage only one side of the collet and produce poor results such as runout and drastically reduced holding strength.
Never try to install a cutting tool with a larger shank than the maximum or nominal diameter of the collet to expand the collet. Most ER Collets are designed to collapse 1mm or .039. For example: If the cutting tool shank is 4.2mm a 4-3mm is not suitable. A 4.5-3.5mm collet would be required.
Sealed ER Collets for coolant through applications do not have a collapse range, and must be used at exact size. The radius of the collet must exactly match the radius of the cutting tool shank in order to maintain a complete seal. If companies claim that they have sealed collets with a collapse range please keep in mind that if the radius does not match exactly coolant canals will be created by the mismatched radius of an improperly sized collet.
RD/ER Collets must be tightened correctly. Many machinists have been trained that nothing is ever too tight. This is particularly not true with collets and collet chucks. Overtightening a collet chuck will distort the collet and actually diminish the holding strength and accuracy. Maximum tightening torque for RD/ER Systems is as follows:
| Series Size RD/ER 11 RD/ER 16 RD/ER 20 RD/ER 25 RD/ER 32 RD/ER 40 |
Max. Tightening Torque (ft. lbs.) 20 40 60 70 80 90 |
 |
Cutting tools should be inserted into the collet the full length of the bore wherever possible. Failure to insert the cutting tool into at least 2/3 of the bore may distort the collet. Collets should be cleaned and oiled prior to storage.
BENEFITS OF ER COLLETS
ER Collets are also very economical when compared with other popular collet systems. Collets work best when used at nominal or full diameter but when the economy is desired this system compares very favorably with other systems. If a user would like to cover a range of 1/8-1″ with a toolholding system please consider that with the RD/ER System this only requires 23 collets. With a TG system of the same capacity it takes 59 collets to cover the same range. When compared with DA collets with a capacity of 1/16-3/4″ the RD/ER system only requires 18 collets while the DA needs 45 collets to cover the same range. This represents a significant cost saving while improving accuracy, and versatility.
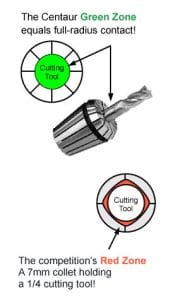
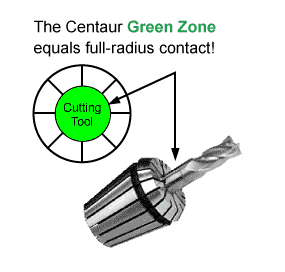
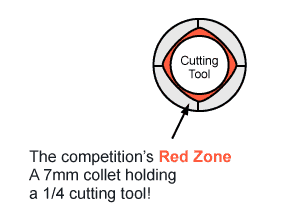
THE CENTAUR “GREEN ZONE”
BENEFITS OF CENTAUR “GREEN ZONE” ER COLLETS
Centaur manufactures the widest variety of exact size collets in the industry to ensure you get the most out of your cutting tools, to reduce downtime and tooling costs.
Centaur offer RD/ER collets in full millimeter sizes, .5mm sizes and true inch size collets in 1/32″ increments from inventory.
Centaur also offers Sealed High Precision Collets for coolant through applications.
Centaur Sealed ER collets are available with internal flow for oil hole tools or, with external flow (coolant canals through the collet) for use with cutting tools with or without oil holes. The external flow collets are especially beneficial for applications where there is coolant through the spindle but lower cost solid cutting tools are desired or applications where oil hole tools are used in through holes.

Centaur external flow ER collets are also extremely beneficial for through holes with oil hole cutting tools, as this will ensure that the cutting is properly cooled completely throughout the entire cycle. In many applications as the cutting tool is passing through or breaking through the workpiece the coolant may be just passing through the hole, with an external flow sealed collet one can be assured the complete cutting edge and lands of the drill are cooled throughout the complete cycle.
Centaur offers the most extensive program for ER tapping collets in the industry. ER Tapping collets will allow users to convert collet chucks used for many purposes into tapping chucks.
Centaur’s ER rigid tapping collets with square drive are available in inch or metric sizes, standard or sealed for internal or external coolant flow.
Centaur also offers RDT/ER tapping collets. These collets will inexpensively convert a standard collet chuck into a length compensating, Quick-change tapping chuck with square drive.
Centaur manufactures each collet from high-grade spring steel and are hardened and fully ground for absolute precision. Each Centaur collet is 100% inspected for the highest possible accuracy.
TG Collets
RDG/TG collets achieve higher accuracy and greater gripping strength than DA collets and some other popular collet systems. This system will perform well in applications up to 10,000 RPM. RDG/TG collets are also known in the industry as DF, BG, VDF, and PG collets.

RECOMMENDED USES OF TG COLLETS
RDG/TG Collets are used for Milling, Drilling and Rigid Tapping. RDG/TG collets are available sealed for coolant through applications. RDG/TG collets. RDG/TG in 1/64” Increments or .5mm increments for metric sized tools.
ACCURACY OF TG COLLETS
RDG/TG Collets are within .0005 T.I.R. The collet chucks are within .0002 T.I.R. from the cone to the collet seat bore. The nuts are designed to float to allow for centering of the collet. RDG/TG systems when properly cleaned and assembled can achieve approximately .001 T.I.R. on a cutting tool shank in the assembly at a checking point length of about 2-3 times the diameter of the cutting tool. The collapse range of the RDG/TG Collets are 1/64”. As with all Collets it is recommended that the collet be used at the nominal or largest diameter. Sealed Collets do not have a collapse range and must be used at the exact size.
CARE AND USE OF TG COLLET SYSTEM
The TG chuck, TG collet and TG nut must be thoroughly cleaned before assembling to maintain accuracy. A benchtop ultrasonic cleaner will dislodge fine chips and debris or, a bottle type brush can be used for cleaning the inner diameter of the collet and a toothbrush style can be used to clean the exterior. Once assembled a normal machining environment will not affect the toolholding assembly.
The RDG/TG Collets must be snapped into the Clamping Nut prior to installing onto the Collet Chuck. Collets can be removed from the clamping nut by holding the small end of the collet and tilting the collet angularly until it is removed from the nut. Do not attempt to remove the collet from the clamping nut by forcing the collet out from the front of the collet nut using a punch or screwdriver as this will damage the collet and clamping nut. For maximum accuracy and holding strength RDG/TG Collets must be tightened correctly, maximum tightening torque is as follows:
| RDG/TG 75 RDG/TG 100 RDG/TG 150 |
80 ft.lbs. 90 ft.lbs. 110 ft.lbs. |
DA Collets

RDA/DA Collets are recommended for drilling. RDA/DA Collets were originally designed to clamp well on slightly uneven surfaces such as jobbers or taper length type drills. RDA/DA Collets are available in 1/64 increments and in .5mm increments for metric sizes. RDA/DA collets are also known in the industry as DA and VDA collets.
RECOMMENDED USES FOR DA COLLETS
RDA/DA collets are recommended for drilling only.
ACCURACY OF DA COLLETS
RDA/DA Collets are manufactured to within .0005 T.I.R. outer diameter to inner diameter. The length of parrallelism between the two female contacting angles in the chuck controls the accuracy of the system and is held to within plus or minus .0002. The clamping nut floats slightly to allow the chuck to center the collet. Normal accuracy is approximately .001 T.I.R at the face of the collet chuck.
CARE AND USE OF DA COLLETS
The DA chuck, DA collet and DA nut must be thoroughly cleaned before assembling to maintain accuracy. A benchtop ultrasonic cleaner will dislodge fine chips and debris or, a bottle type brush can be used for cleaning the inner diameter of the collet and a toothbrush style can be used to clean the exterior. Once assembled a normal machining environment will not affect the toolholding assembly.
AF Collets

This highly accurate Acura-Flex collet system (AF collet system) was originated by Universal Engineering. RDF/AF Collets are recommended for drilling, milling and boring applications. RDF/AF collets are also known in the industry as BF collets.
AF collets are available in 1/64” increments and limited metrics sizes. RDF collets are designed to collapse 1/64. Size ranges are as follows:
| Series RDF 25 RDF 38 RDF 50 RDF 75 RDF 100 |
Inch Range 1/32-1/4 1/16-3/8 7/64-1/2 7/64-25/32 13/64-1” |
*RDF/AF Collets in the 50, 75 and 100 series are available sealed for Coolant through applications.
RDO Collets DIN 6388 Style

The high gripping strength RDO collet system was originated in Europe and are sometimes known as Ortlieb style collets or Full Grip Collets. Many machines designed for woodworking also use this system. This system is recommended for milling, drilling and boring applications. Many high production routing systems manufacturers have standardized on this system. Size Ranges are as follows:
| Series RDO 16 (form A style) RDO 20 RDO 25 RDO 35 RDO 44 |
Inch Range 1/8 – 3/8 1/8 – 1/2 1/16 – 5/8 1/8 – 1″ 1/8 – 1″ |
Metric Range — 2mm – 13mm 2mm – 16mm 2mm – 25mm 4mm – 32mm |
*RDO 25, 35 and 44 series collets are available sealed for coolant through applications.
Glossary & FAQ
What is a collet?
A collet is a device used in a collet chuck to clamp on a cutting tool.
What are collets made of?
Centaur manufactures each collet from high-grade spring steel and are hardened and fully ground for absolute precision.
What is a collet used for?
Collets are used to hold smaller workpieces (ranging from 1/16″ to 2.5″) and have a narrow clamping range (~1mm).
What does collet size refer to?
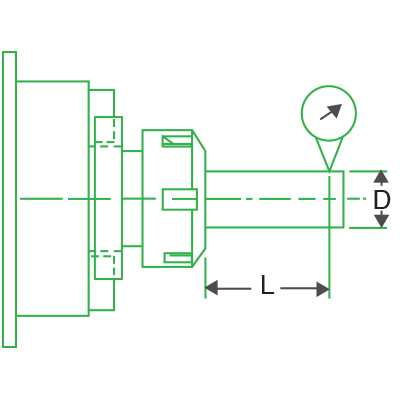
Collet size usually indicates the size tool the collet will hold. (e.g. ER16 will hold a tool that is 16mm in diameter). Refer to the collet sizes chart below for some common measurements:
ER Collet Sizes
| Collet Series | Length | Diameter |
| ER11 | 18 mm (.708″) | 11.5 mm (.45″) |
| ER16 | 27.5 mm (1.08″) | 17 mm (.67″) |
| ER20 | 31.5 mm (1.24″) | 21 mm (.83″) |
| ER25 | 34 mm (1.34″) | 26 mm (1.02″) |
| ER32 | 40 mm (1.57″) | 33 mm (1.3″) |
| ER40 | 46 mm (1.81″) | 41 mm (1.61″) |
TG Collet Sizes
| Collet Series | Length | Diameter |
| TG 75 | 47 mm (1.85″) | 27 mm (1.06″) |
| TG 100 | 60 mm (2.36″) | 35 mm (1.38″) |
How do I know what type of collet I have?
Measure the length and diameter of the collet. All collets have a distinctive length and diameter. Here are some common collet types and dimensions:
ER Collet Sizes
| Collet Series | Length | Diameter |
| ER11 | 18 mm (.708″) | 11.5 mm (.45″) |
| ER16 | 27.5 mm (1.08″) | 17 mm (.67″) |
| ER20 | 31.5 mm (1.24″) | 21 mm (.83″) |
| ER25 | 34 mm (1.34″) | 26 mm (1.02″) |
| ER32 | 40 mm (1.57″) | 33 mm (1.3″) |
| ER40 | 46 mm (1.81″) | 41 mm (1.61″) |
TG Collet Sizes
| Collet Series | Length | Diameter |
| TG 75 | 47 mm (1.85″) | 27 mm (1.06″) |
| TG 100 | 60 mm (2.36″) | 35 mm (1.38″) |
How does a collet work?
Collets use clamping pressure by forming a collar around the tool being held, providing a stronger grip and better accuracy.
How do I remove a collet from collet nut?
Removal can differ depending on the collet style used. For ER collets, hold the nut in the vertical position (diamonds/triangles in the 12 o’clock position) and press down on the collet. The collet should snap out.
What is the difference between a collet and a chuck?
Uses:
Collets are best for gripping smaller workpieces (ranging from 1/16″ to 2.5″) compared to chucks, which are better suited for gripping larger parts or parts with inconsistent diameters.
Structurally, chucks are designed to be tightened around an object. In contrast, collets use clamping pressure by forming a collar around the tool being held.
What are the advantages of using a collet chuck?
Compared to standard 3-jaw chucks, collet chucks are more affordable, perform better at higher RPMs, have faster changeover, better concentricity, greater accuracy. and are best suited for gripping small parts.
4 Advantages of Collet Chucks:
1. Spindle performance. Compared to the large jaw chuck, the collet chuck’s smaller size allows for faster acceleration, making it the best choice for turning at high spindle RPMs.
2. Tight tolerances. Collet chucks do not suffer the reduce clamping force caused by centrifugal force that affect jaw chucks.
3. Changeovers. Collet chucks can be changed in 20 seconds, while jaw chucks may take as much as 20 minutes to change.
4. Small parts. Collet chuck are best for machining smaller parts, due to their better grip, weight, acceleration and changeover speed. Standard 3-jaw chucks are great for larger parts, objects with inconsistent diameter, larger axial dimensions, or when working with a large variety of work pieces.
How does a collet chuck work?
A collet chuck clamps a collet by tightening the clamping nut.
How are chucks used?
A chuck is a specialized type of clamp used to hold an object with radial symmetry, especially a cylinder. In drills and mills it holds the rotating tool whereas in lathes it holds the rotating workpiece. On a lathe the chuck is mounted on the spindle which rotates within the headstock. [source: everythingwhat]
What is a three-jaw chuck?
A three-jaw powered chuck is the standard workholding device for most CNC lathe users.
What's the difference between a standard collet chuck and a spring collet chuck?
Standard collet chucks consist of a round flat backplate with either four or six arms rising up around the plate’s circumference.
Spring collet chucks don’t have backplate and arms, instead the chuck is a hollow cylinder, much like a sized attachment for a socket wrench.
[source: ehow]
What is the difference between ER collets and TG collets?
More tool holders are available in ER style than TG style.
ER collets are more affordable than TG collets.
ER collets have better range than TG collets.
Both ER collets and TG collets have about same TIR accuracy.
What is the difference between ER and RD collets?
RD was Centaur’s designation for ER Collets. They are the same.
What is a router collet?
A router collet is a collet used to clamp router bits in a router. The collet works with the collet nut and the router shaft (connected directly to the motor) .
What are collet closers?
Collet closers remove unnecessary repetitive steps from the process of working with lathes, grinders, and CNC rotary tables.
What is a 5C collet?
A 5C collet is workholding style collet normally used in lathes.
What does ER collet mean?
Rego-Fix created and patented the ER collet in 1972. The R in “ER collet” stands for Rego-Fix, representing the company’s modification to the E collet design: a groove that allows easier removal than the original E collet.
What is an ER11 collet? What is an ER20 collet?
The number following ER refers to the collet’s range. An ER 11 is a collet that has a range of 0.5-7mm or 1/16″ -1/4″. An ER 20 is a collet that has a range of 0.5-13mm or 1/16″-1/2″.
What is TIR?
Total Indicator Reading (TIR), is the difference between minimum and maximum readouts found when an indicator is run along the surface of a part while it is rotated along an axis. The TIR measures any discrepancy found in the planar, cylindrical, or contoured surface of a part. TIR is important for testing whether the flatness, circular, concentric, or any other shape for a part is maintained precisely or whether adjustments need to be made before the part can be used in a bigger machine.
What are Centaur Certified Collets?
Centaur manufactures each collet from high-grade spring steel and are hardened and fully ground for absolute precision. Centaur Certified Collets are 100% inspected for Function and Concentricity with specialized in-process and post-process gaging. They are certified to be within published specifications.
What is the Centaur "Green Zone"?
The Centaur Green Zone refers to full-radius contact design that centralizes the cutting tool. This provides concentricity that increases tool life, enhances feed rates and rpm, and improves workpiece accuracy and finish.